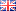
Igniters
One of the main processes in starting a gas turbine is the process of igniting the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber.
The most commonly used igniters for this purpose were.
Inside the igniter, a spark discharge occurs between the electrodes. A high-voltage wire is installed inside the protective refractory procedure.
The main characteristic of the igniter is the bag temperature. It must ensure reliable ignition of the fuel-air mixture of the design capacity. If the igniter fails to ignite, the fuel-air mixture will be fed into the flowing part and its concentration will continuously increase. In order to reduce the gas voltage when the igniter fails, it is necessary to cut off the gas supply and purge the flowing part. Only after this complex work is done can the ignition be re-ignited.
The igniter is most often installed in the side wall of the flame tube.
The igniter control unit is connected to the GTU control system, which allows to control the production process.
The design of igniters should be as simple and reliable as possible in order to ensure efficient ignition of the fuel-air mixture.